A Comprehensive overview to the Physiotherapy Exercises
Are you in pain or have any injuries? You must be looking for the best possible solution for the problem. Eating medicines has come with a lot of side effects. Physiotherapy is a more popular approach to getting rid of pain and injury in today’s age.
Physiotherapy is done by a specially trained person known as a physiotherapist. Various kinds of exercises are also performed in physiotherapy. You can also perform these exercises by yourself.
Introduction To Physiotherapy Exercises
Physiotherapy includes non-pharmacological interventions in different types of clinical situations. It is used for various medical problems, illnesses, or injuries. It is more effective to overcome illness and injury without using the medicine.
Physiotherapy exercises benefit joint pain, regardless of whether you have more chronic pain from osteoarthritis or an immediate sporting injury. Joint pain is frequent during growth spurts in children, with accidents in sports or falls, or it can appear as we age from wear and tear.
It can be brought on by muscles, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, or meniscus. It can also sometimes refer to the lower back, knee, or the hip joint. Your physiotherapist will perform a thorough assessment to identify the origins and aggravating elements of your pain. At Prime Physio Care, we might advise physiotherapy exercises to relieve some of the strain and add a little extra support.
List of a Few Physiotherapy Exercises
Joint pain can make engaging in your favorite activities challenging, whether you’re a devoted walker, weekend warrior, or competitive athlete. The discomfort is a frequent problem. Osteoarthritis, tendinitis, bursitis, a torn meniscus, and sprained ligaments are the discomforts that fall under this category. The good news is that joint discomfort is treatable, and self-care stretching and strengthening physiotherapy exercises are among them.
-
Stretching Exercises
Your joints’ range of motion and flexibility may improve with lower body stretching physiotherapy exercises. Before stretching, you must warm up for at least 5 to 10 minutes. After warming up, please perform the following three stretches, then repeat them after you have finished the knee-strengthening exercises. At the very least, try to do these stretches and physiotherapy exercises four or five times per week.
-
Hamstring Stretch

Hamstring Stretch
This stretch primarily targets your hamstrings and the muscles in the back of your thigh. Your glutes and the back of your leg should both feel comfortable during this stretch. Flexing your foot may cause your calves to feel stretched as well. Pair a mat underneath you to make this stretch more comfortable for your back. Place your hands behind your thigh but below the knee and gently draw your knee toward your chest until you feel a slight stretch. Repeat twice, once on each side.
-
Half Squat
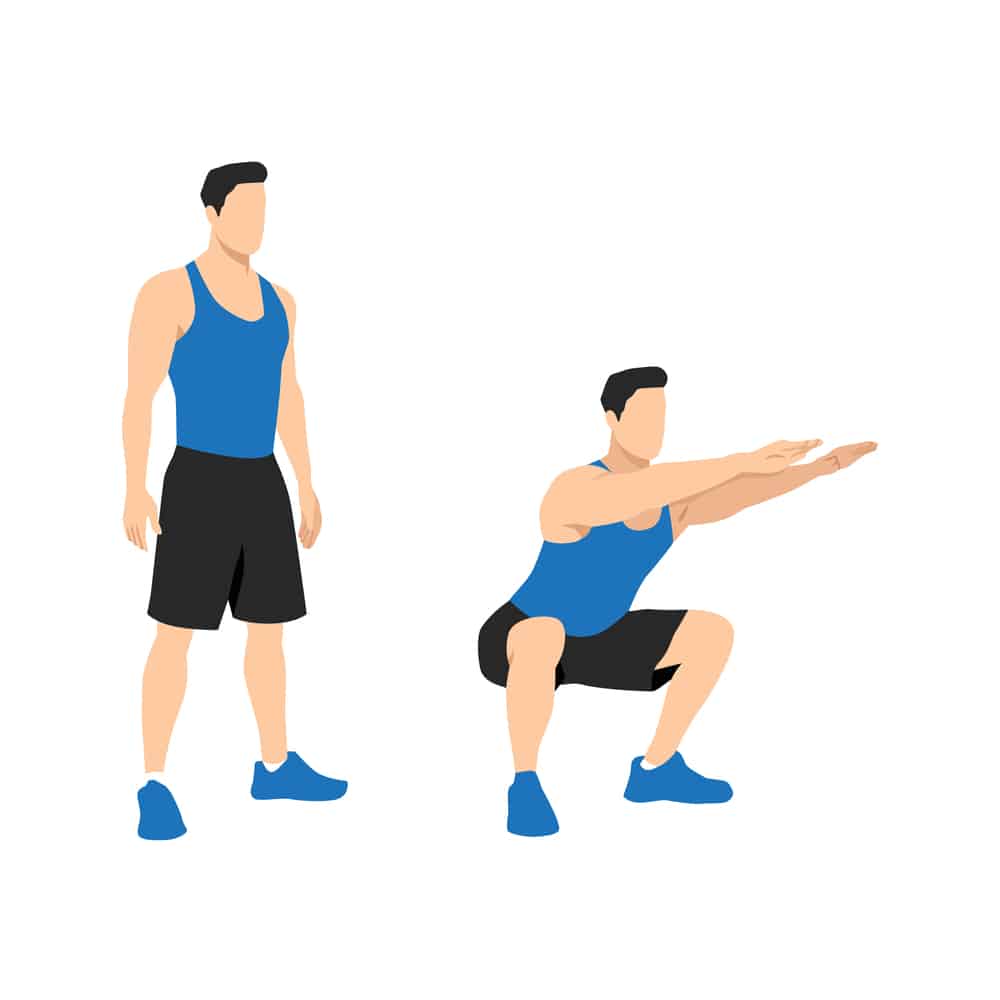
Half Squat
The half squat is a beautiful workout for strengthening your quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings without putting too much strain on your knees. To finish this task, squat down with your feet shoulder-width apart. Attempt two or three sets of ten repetitions each.
-
Calf Raises
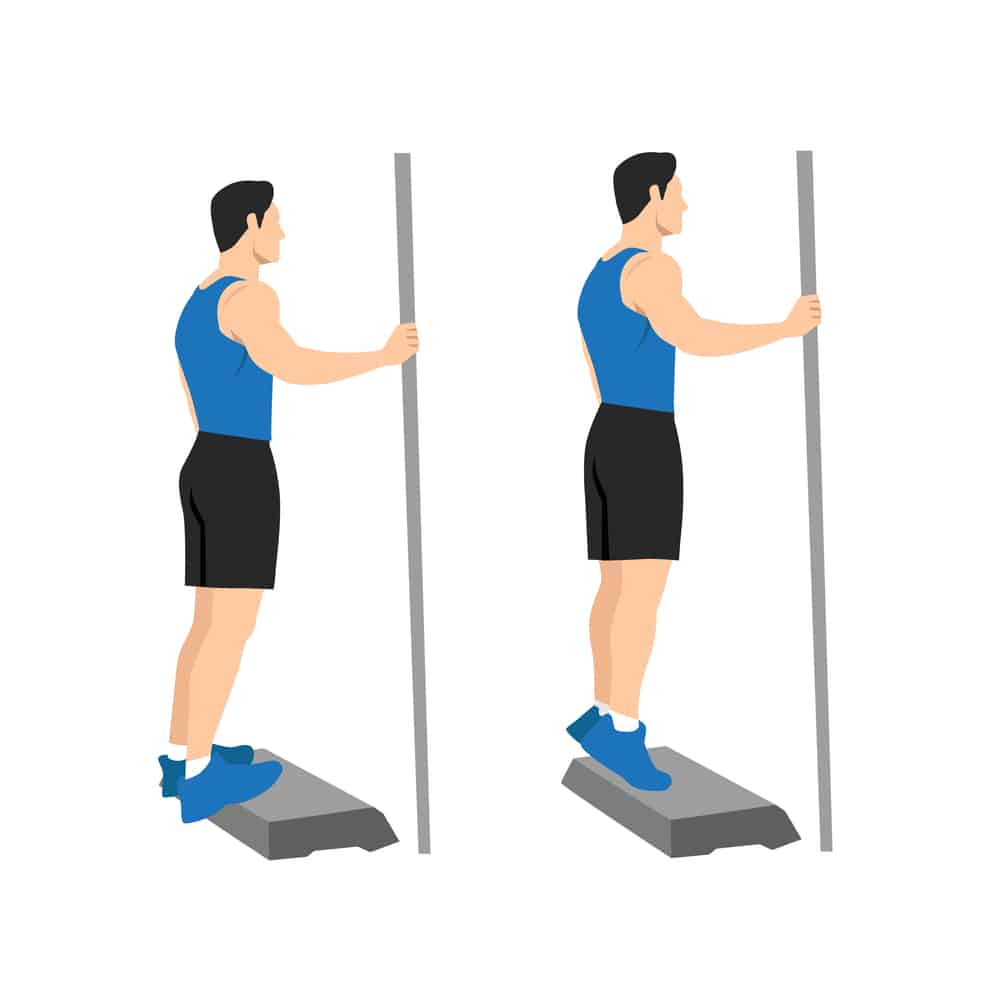
Calf Raises
This exercise helps to strengthen the calf muscles found on the back of your lower legs. To finish this task: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Lift both of your heels off the floor and stand on the balls of your feet. Control is essential when completing this workout to build your calf muscles. Attempt two or three sets of ten repetitions each.
-
Leg Extensions
Leg Extensions
You can lessen the pressure on your knees by strengthening your quadriceps using your body weight rather than a weighted machine. Lift one leg as high as possible without getting out of the chair by straightening your spine and contracting your thigh muscles, and doing so.
The Different Types Of Exercises In Physiotherapy
The physiotherapist plans the workouts based on the patient’s condition. Before making a provisional diagnosis, they carefully consider the patient’s complaint, go over their recent and historical medical histories, and perform a thorough evaluation of the patient. They develop a treatment plan based on this early diagnosis. Some of the most popular physio exercises categories are listed below:
-
Resistance Exercises
These workouts call for the application of some resistance. Weights, gravity, and elastic bands are just a few of the numerous causes of resistance. When under stress, your body adjusts, and when you urge your muscles to accomplish something they are not used to, they respond by getting stronger.
Our muscles will adapt to this and stop growing, most likely deteriorating, if we don’t challenge them as we age, either by exercising less or doing the same things every day. Therefore, it is likely that your muscles are degrading if you spend the entire day at a computer desk.
-
Stretching Exercises
These physiotherapy exercises are intended to improve flexibility. By drawing away from the muscle’s insertion and origin, the goal is to stretch it. For these workouts to be effective, the compensations must be corrected, and you must align the body segments. Furthermore, letting out your entire breath to relax your muscles and lessen resistance is essential. The stretching positions are held for lengthy periods with minimal repetitions.
-
Strengthening Exercises
Increases in muscle power, strength, and endurance all occur. You can utilize them to mobilize stabilizers or other types of muscles, two distinct categories of muscles, with or without a load (hands-free), a load, or using your body weight, dumbbells, elastic bands, pulley systems, etc.
-
Functional Exercises
Specialized physical rehabilitation exercises known as functional activities are advised to practice complex daily movements after an injury. The physiotherapist may ask you to replicate a particular motion that you employ in your sport, at work, or at home if required.
-
Balance and Neuromuscular Exercises
This kind of exercise improves the communication between your neurons and muscles. Among other things, they aid in enhancing knee stability in athletes or preventing falls in the elderly. The communication between your muscles and nerves is disrupted by an injury, which inhibits your body from responding as it should. If you’ve ever felt a lot of instability following a joint injury, that might be the cause.
Patients are told that it functions akin to turning on a light in a room full of other lights. If you have an injury, the switch and those lights don’t communicate well, so when you flip the switch, only a third of them light up, another third flicker, and the last third remains dark. Through neuromuscular training, this connection is made more robust so that when the switch is flipped, all the lights, or muscle fibers, turn on.
Physiotherapy Massage
Massage is a manual method that helps to reduce muscle tension and promote healing. Trigger point treatment usually works together. Deep friction massage is the most frequently used type of massage in physiotherapy, even though there are numerous other physio massages near me. This method involves pressing firmly into the muscle to alleviate tension and promote recovery.
It can massage deep muscles to release tension after an accident or a strenuous workout. Muscles become damaged after an accident or a period of vigorous use, and they contract to speed recovery and offer defense against further damage. Scar tissue is also produced during the healing process, making muscles less flexible.
Deep friction physio massage breaks down scar tissue, enabling the muscle to move more freely. Additionally, it promotes muscle relaxation, which quickens the healing and recovery process. You might experience some soreness for a few days after the physiotherapy massage, but you should quickly start to feel better.
Modes of Therapeutic Massage
-
Stroking
When striking, either the entire hand or just the fingers are utilized. It entails using a hand that is at ease to softly rub the patient’s skin in a rhythm and pressure that has a relaxing effect.
-
Kneading
The manipulable part is frequently compressed and released during kneading.
-
Picking Up
The tissue is squeezed before being released when picked up, having been raised off the underlying bone.
-
Wringing
The tissue is lifted and turned to increase the stretching effect while wrung out.
-
Friction
Friction puts pressure on the tissue from the surface to the depth with a slight movement of the thumb or finger.
-
Hacking
Hacking entails extending the forearm and striking the skin with the side of the hand.
-
Clapping
Clapping is done by smacking the skin with cupped hands.
-
Vibration and Shaking
Shaking and vibration, on the other hand, are mild vibrations and shakes.
Neuro Physiotherapy Exercises
Neuro physiotherapy exercises include rehabilitation for people with neurological conditions. Neurological problems are issues that affect the brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nerves. Physical abilities like mobility, muscle strength, range of motion, and balance may be troublesome for people with neurological issues.
-
Brushing
Quick brushing is a therapeutic technique to enhance static holding postural extensors and facilitate movement responses by employing a battery-operated brush on the skin above the muscle. There is a minimal study on brushing’s effectiveness, its long-term consequences, how often, for how long, and at what pressure this should do.
-
Joint Compression
Compression of the joints may improve joint awareness, enhancing motor control. Muscle and joint receptors that are involved in the perception of joint position and movement are stimulated by joint compression. Joint compression can both facilitate and impede some processes. Joint compression of the joint surfaces facilitates the extensors necessary to stabilize the body’s posture.
Apply compression jerkily to improve muscular control; apply compression steadily to impair muscular control. Both manual application and weight-bearing postures are feasible. Compressing a joint can be accomplished in two ways:
-
Light Compression
It is believed that typical body weight applied across the long axis of a bone will reduce (inhibit) muscle stiffness.
-
Heavy Compression
It is suggested that co-contraction during joint compression be made more accessible by more compression than that caused by body weight.
-
Muscle Vibration
Muscle vibration has been used to treat neurologically unwell patients to reduce stiffness and tone. Corticospinal excitability and inhibitory neural activity are thought to rise in response to muscle vibrations in the antagonistic muscle. It helps the vibrating muscle contract by activating the tonic vibration reflex. The other neurons that supply the antagonistic muscles are repressed through antagonistic or reciprocal inhibition—monosynaptic stretch reflex inhibition during muscle vibration.
-
Whole Body Vibration
A relatively new modality called whole body vibration, which involves vibrating while standing on a vibrating platform has been utilized to improve balance and gait. Future well-designed tests with a bigger sample size will need additional studies on the optimal frequency, amplitude, and duration of vibration application in neurorehabilitation.
Rehabilitation Exercises
Rehab exercises reduce inflammation, decrease pain, boost mood, and lessen stress and fatigue. It also improves sleep quality, prevents falls, and promotes balance. It is a muscle relaxant that improves focus, sleep, bone health, and immune system power.
Dementia, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, incontinence, and the number of cancers are also reduced. The three main types of rehabilitation therapy are speech, physical, and occupational. Each rehabilitation has a purpose that aids the patient’s full recovery. However, they are all designed to help the patients return to their everyday, active lifestyles.
Occupational Therapy
Treatments are provided by occupational therapists (OT) to help those who require exceptional support engage in routine tasks or “occupations.” Occupations can apply to everyday tasks, leisure activities, and self-care routines in addition to work or your profession.
Occupational therapists help by addressing issues that prevent a person from performing daily tasks, including eating, dressing, cleaning their teeth, finishing their schooling, and working. Therapists can make modifications by changing the way an activity is carried out, the environment in which it is carried out, or by helping someone develop the skills necessary to execute particular tasks.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is widely used to treat long-term diseases like heart disease or arthritis, manage pain, enhance movement, provide rehabilitation after a stroke, an injury, or surgery, help with postpartum recovery, and various other purposes. Additionally, it can instruct users on how to use walking aids and canes.
Speech Therapy
Speech therapists, often called speech-language pathologists, provide treatment for people with speech issues. Neonatal patients who struggle to drink, swallow, or communicate due to conditions including cerebral palsy, cleft palate, or Down syndrome can receive help from a speech therapist.
Adults who struggle to learn or suffer from conditions like dementia, Parkinson’s disease, a stroke, or cancer of the neck or head can benefit from the services of a speech therapist. Integrating language use and speech mechanics is the goal of speech therapy.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy aids those who have lost movement and function due to an illness, injury, or disability. In addition, physiotherapy assesses, diagnoses, treats, and aims to prevent illness and impairment as a career in healthcare.
Physiotherapists help people who have been hurt, are ill or are disabled move around, do physiotherapy exercises, receive manual therapy, receive education, and get counseling. They help patients manage their pain and avoid illness, maintaining their health and that of all age groups.
How can you book an appointment?
We aim to see you within 24 hours so contact us to make an appointment either online at www.primphysiocare.co.uk or to find out more information on how we can help you, please call us on 07515280990 or email us primephysiocareluton@gmail.com. We are one of the best clinics whose physios are registered with HCPC, CSP and Physio first as well have enormous experience.
FAQ’s
Q: Which form of physical treatment is best?
Orthopedic physical therapy is the most often used form of physical therapy. It has the broadest scope of subjects covered. Sports physiotherapists treat sports injuries with orthopedic procedures. For anyone recovering from surgery on their bones or muscles, we do, however, recommend this course of action.
Q: What exactly is a physical therapy exercise?
Exercise therapy involves physical activities to increase comfort, strength, and function. Your physiotherapist may incorporate exercise therapy into your treatment plan if you are undergoing physiotherapy for an injury or a chronic condition.
Q: How do I perform physical therapy at home?
A typical form of treatment for physiotherapists is exercise. Perform a few easy at-home physiotherapy exercises for your feet, neck, and back to assist yourself. How to increase the impact of these workouts Each exercise should be performed at least five times, with the number rising over time.
Q: What varieties of physiotherapy are there?
A few types of physiotherapy includes, cardio physiotherapy, sports physiotherapy, rehabilitation and pain management physiotherapy, skeletal muscle and bone physiotherapy.
Q: What do the physiotherapy free exercises entail?
Free workouts are ones that patients perform solely with their muscular strength, without the assistance of or resistance from any external force other than gravity.
Q: What is fundamental physical therapy?
Physiotherapy enhances a patient’s mobility, functionality, and general well-being. The advantages of physiotherapy include physical rehabilitation, injury prevention, and health and fitness. You are involved in the healing process by the physiotherapists.